|
ObjectDataSource
Control
The large web application
are normally layered as,
· Presentation Layer
· Business Objects
· DAL
Our previous examples in Part 1 does
everything in ASP.Net Page itself and also it has some disadvantages like if the
underlying the table schema changes then we have to re configure the Datasource
control.
For doing the above with ObjectDataSource control we have to design an
entity (Business Object) and DAL to access the DB. In our example it is Employee
and EmployeeDAL.
Employee.cs
public class Employee
{
#region Private
Members
private int empid;
private string fname;
private string
lname;
private string gender;
private DateTime
dob;
#endregion
#region Public Properties
public int
EmpID
{
get
{
return empid;
}
set
{
empid =
value;
}
}
public string FirstName
{
get
{
return
fname;
}
set
{
fname = value;
}
}
public string
LastName
{
get
{
return lname;
}
set
{
lname =
value;
}
}
public string Gender
{
get
{
return
gender;
}
set
{
gender = value;
}
}
public DateTime
DOB
{
get
{
return dob;
}
set
{
dob =
value;
}
}
#endregion
}
EmployeeDAL.cs
public static void UpdateEmployee(int empid, string
firstname, string lastname, string gender, DateTime dob)
{
//For
Update
}
public static List Getemployee(string sortexp)
{
//For
Sorting
}
public static List Getemployee(int maximumRows,int
startRowIndex,string sortexp)
{
//For Paging
}
public static void
DeleteEmployees(int Empid)
{
//For Deleting
}
|
|
|
Steps for using
ObjectDataSource Controls
1) Drag an
ObjectDataSource and Gridview Control from the data tab in visual studio.
2)
Click Configure Datasource and set the DAL as shown in figure. Click
Next.
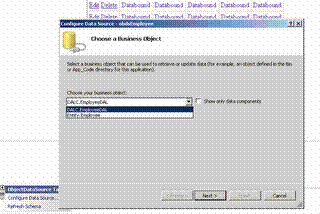
3) Select the select, update and delete methods as shown
in figure and Click Finish as shown in Figure.
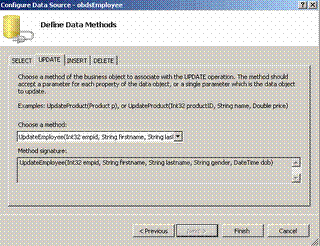
4) Set the DatasourceID of the Gridview to Datasource ID
of the Object Datasource.Set Paging,Editing,sorting and Deleting.
5) Run the
application.
Things to
Remember
Update
Make sure that the column name in Gridview and the
arguments of the Update Method are same. The signature for the Update method
depends on the ObjectDataSource's ConflictDetection property. If you are using
the default behavior OverwriteChange then the Update method needs to accept
the original primary key field(s) along with parameters for the non-primary key
updated values. If, on the other hand, CompareAllValues is used, the Update
method must accept both the updated and original non-primary key field values
along with the original primary key field(s).
Sorting and Paging
For a pageable GridView from an ObjectDataSource the
underlying DAL class's SELECT method must accept the following inputs: the first
one specifying the maximum number of records to return as int and the second
specifying the starting record index as int and the third one will be
SortExpression as string. The following parameters should be set in
ObjectDatasource for Sorting and Paging to work.
EnablePaging, set this to true.
MaximumRowsParameterName, this property provides
the name of the first integer parameter to the method that pages the results. It
defaults to maximumRows. If you use a different parameter name in your methods,
you'll need to specify that parameter name in this property.
StartRowIndexParameterName is similar to
MaximumRowsParameterName, in that this property value specifies the second
integer parameter name for paging. It defaults to startRowIndex, so we need to
set this property explicitly if we use a different parameter name in your code.
SelectCountMethod is the name of the
method that returns the total number of records to be paged through.
SortParameterName is the name of the string
input parameter specifying how to sort the data. In my example I used sortexp.
Deleting
Specify the
DataKeyNames to Primary key filed in GridView Property.
XmlDataSource
For understanding the
XmlDataSource we need an XML data file.
Steps for using XmlDataSource controls
1) Drag a GridView and XmlDatasource controls from the
toolbox.
2) Configure the XmlDataSource to get the data from an xml source
as shown below.
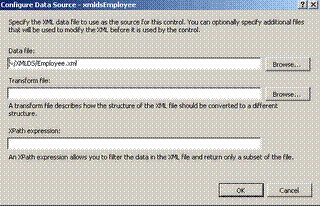
The above window shows 3 textbox but specifying data file
alone will do.
The above window takes,
1. The path to the XML file, which is required.
2.
The path to an XSD file that defines the schema for the XML file. You do not
need to provide a schema, as the XmlDataSource does not use schema information
at all. However, a data Web control might require type-specific information,
which the schema file provides.
3. An optional path to an XSL transform
file. If the XML in the file does not conform to a structure you want, you can
specify a translation through this XSL transform file setting.
4. An
optional XPath expression, useful for filtering the data returned by the
XmlDataSource. By default, the entire contents of the XML file will be loaded by
the XmlDataSource. By specifying an XPath expression, however, you can limit
those elements retrieved.
|